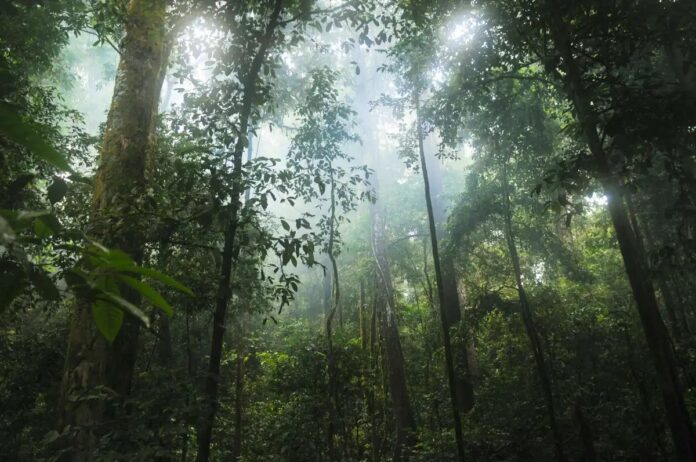
Google is taking a significant step toward achieving its carbon neutrality goals by investing in a large-scale reforestation project in the Amazon rainforest. The tech giant announced Thursday it will purchase 200,000 metric tons of carbon removal credits from Mombak, a Brazilian company specializing in forest restoration.
The Mombak Project and the Symbiosis Coalition
Mombak’s project focuses on acquiring farmland within the Amazon and actively reforesting it. This initiative is being facilitated through the Symbiosis Coalition, an advance market commitment aimed at fostering a marketplace for nature-based carbon removal solutions. Several major corporations – including Google, McKinsey, Meta, Microsoft, and Salesforce – are backing the Coalition. This model, similar to Google’s Frontier initiative supporting direct air capture, provides upfront funding to encourage the development of these projects. The goal is to create a reliable and scalable market for companies seeking to offset their carbon footprints through natural solutions.
Why Nature-Based Carbon Removal Matters
Nature-based carbon removal offers a promising avenue for reducing atmospheric CO2 levels. Unlike technologies like direct air capture, which extract CO2 directly from the air, these projects leverage the natural ability of forests to absorb and store carbon. However, the development and sale of these credits haven’t been straightforward. A key challenge lies in ensuring the long-term success of these projects, as they can be vulnerable to natural disasters like wildfires, which can diminish their ability to store carbon. Guaranteeing their sustained effectiveness over decades is essential for their credibility.
More Than Just Carbon: Biodiversity and Ecosystem Benefits
Beyond carbon sequestration, reforestation projects offer a range of additional ecological benefits. Forests play a vital role in replenishing groundwater supplies and supporting biodiversity, advantages that are absent in technologies like direct air capture. Recognizing this, Google plans to employ its DeepMind Perch AI system to help quantify and track the biodiversity benefits derived from the Mombak project. This is a step towards more comprehensive evaluation of nature-based climate solutions.
The investment in the Amazonian reforestation project highlights a growing recognition that tackling climate change requires a multi-faceted approach, leveraging both technological innovations and the power of natural ecosystems.
This agreement between Google and Mombak represents a substantial investment in a vital ecosystem and underscores the potential for companies to support nature-based solutions to address climate change, moving beyond solely relying on technological fixes. The effort shows a commitment to a broader view of carbon offsetting, factoring in ecological health alongside emissions reductions.